Sjogren’s syndrome Test and Diagnosis
Sjogren’s syndrome can be diagnosed using a combination of clinical evaluation models and specific laboratory tests.
The test and diagnostic process of the disorder involve the following.
Using the Medical history of the patient and physical examination
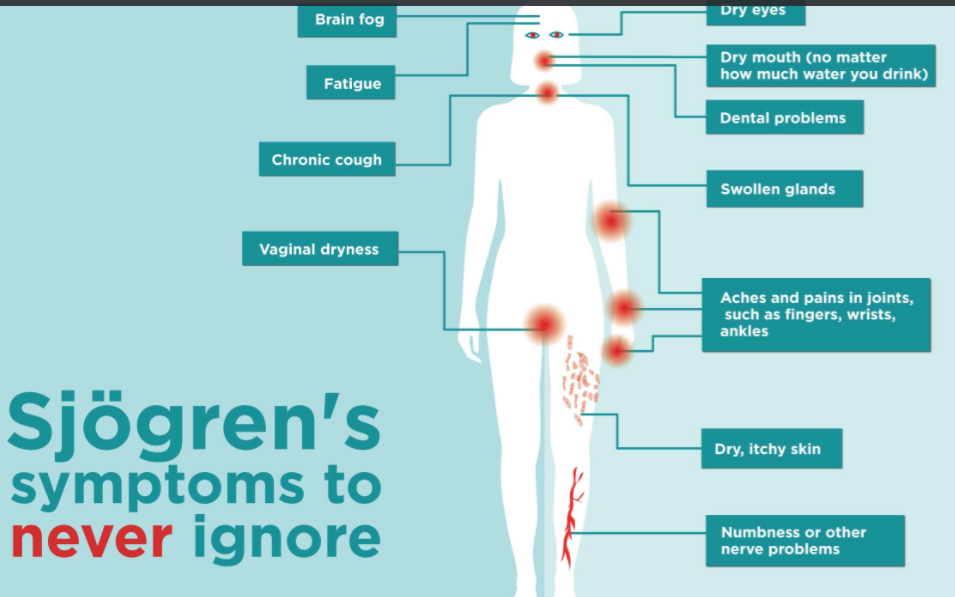
Your doctor will check and review your medical history, and may also ask if the disorder has occurred to any member of your family in the past.
He further performs a physical examination to assess for signs of dryness in the eyes, mouth, and other areas of the body to determine the symptoms of sicca syndrome.
Schirmer’s test for Sjogren’s syndrome
Schirmer’s test is another procedure to test sSjogren’ssyndrome. Schirmer’s test measures the number of tears produced by the eyes.
Your doctor would interpret the result as positive or negative. If positive, it means the amount of tears produced by the eyes is far below normal, meaning there’s a persistent dryness of the eyes.
Salivary gland biopsy
Lip or labial salivary gland biopsy findings can also be used to test the presence of sicca syndrome.
A small sample of tissue can be taken from one of your salivary glands to check for signs of inflammation or damage.
While it may not be the main test to determine Sjogren’s syndrome, it can be used to complement other diagnoses.
Blood tests for Sjogren’s syndrome
Specific blood and urine tests are used to look for certain antibodies that are associated with Sjogren’s syndrome, such as anti-SSA and anti-SSB.
A combination of ultrasound imaging, biopsy, and Antinuclear antibody is the most accurate test for Sjogren’s syndrome as it finds changes in the salivary glands and the antibodies responsible for the disorder.
Other tests: Depending on the individual’s symptoms, other tests such as imaging studies, lung function tests, or nerve conduction studies may be recommended to assess the extent of organ involvement.
A diagnosis of Sjogren’s syndrome is made when an individual meets the established criteria for the condition, which includes a combination of symptoms, physical exam findings, and laboratory test results.
Sjogren’s syndrome Treatment
There seems to be no cure for Sjogren’s syndrome, although it can be efficiently controlled.
Various Sjogren’s syndrome treatment forms aim to relieve the symptoms of the autoimmune disorder, prevent complications, and improve the quality of life of the person affected.
You should maintain good health and have ha healthy lifestyle so the body’s immune system can be able to recognize attackers such as germs and viruses.
Treatment of Sjogren’s syndrome may include the following
-
Using artificial tears and saliva
These products can help relieve dryness in the eyes and mouth.
-
Medications
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce joint pain and inflammation, while medications that stimulate saliva production may be used to improve dry mouth symptoms.
-
Immunosuppressive drugs
In some cases, medications that suppress the immune system may be used to reduce inflammation and prevent organ damage.
-
Pilocarpine and cevimeline
These medications can help stimulate the production of saliva and improve dry mouth symptoms.
-
Moisturizing agents
Lotions, creams, and ointments can help relieve dry skin.
-
Dental care
Regular dental care, including fluoride treatments, can help prevent dental complications associated with dry mouth.
-
Eye care
Regular eye exams, and the use of prescription eye drops, may help prevent eye complications associated with dry eyes.
In addition to medical treatment, lifestyle changes such as drinking plenty of fluids, avoiding caffeine and alcohol, and avoiding smoking can also help manage Sjogren’s syndrome symptoms.